Utilities
Table of contents
Helpers
The udon2.helpers module provides useful functions that operate beyond the level of one node (or subtree induced by this node).
Finding common ancestor
New in v0.1.0
find_common_ancestor(n1, n2) is a helper returning a common ancestor in the depdenency tree between the nodes n1 and n2. The function expects both nodes to be in the same tree and returns the instance of udon2.Node class. To give an example, consider the dependency tree shown in the figure below and the associated code snippet.
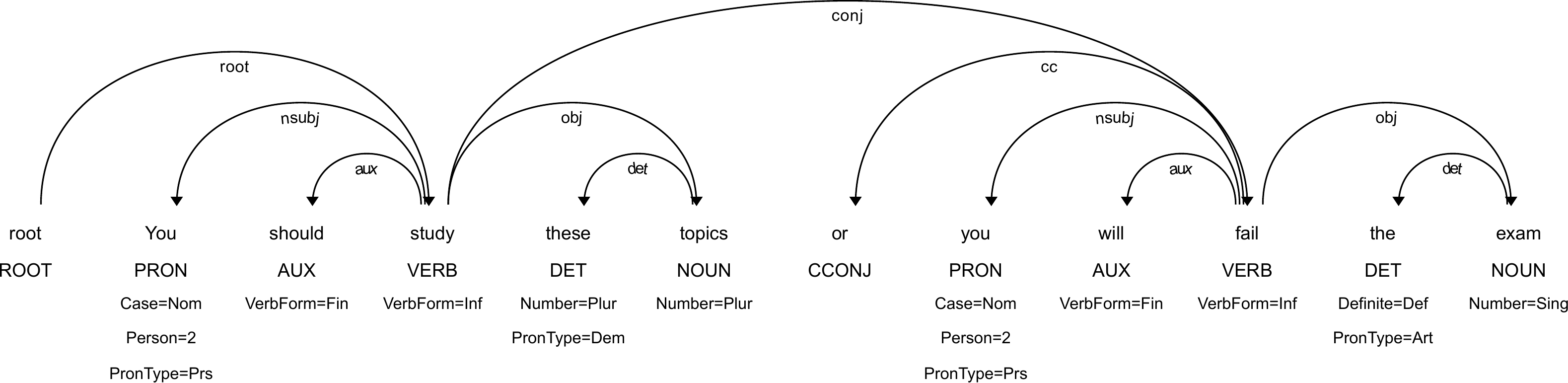
import stanza
import udon2
from udon2.helpers import find_common_ancestor
en = stanza.Pipeline(lang="en", processors='tokenize,lemma,pos,depparse')
roots = udon2.Importer.from_stanza(en("You should study these topics or you will fail the exam.").to_dict())
r = roots[0]
n1 = r.select_by("form", "or")[0]
n2 = r.select_by("form", "exam")[0].children[0] # "the" near the exam
print(str(find_common_ancestor(n1, n2))) # prints "VERB|conj|fail"
Getting a chain of DEPRELs between the nodes
New in v0.1.0
If you have two nodes n1 and n2 in the same tree, then get_deprel_chain(n1, n2) will return a chain of DEPRELs between the nodes. Since all arcs in the dependency tree are directed, the function considers both the direct chain (from n1 to n2) and the reverse chain (from n2 to n1). The function returns the udon2.Chain structure that has two attributes: direct - for the direct chain and reverse for the reverse chain. The example below is given for the same dependency tree as in the previous section.
import stanza
import udon2
from udon2.helpers import get_deprel_chain
en = stanza.Pipeline(lang="en", processors='tokenize,lemma,pos,depparse')
roots = udon2.Importer.from_stanza(en("You should study these topics or you will fail the exam.").to_dict())
r = roots[0]
n1 = r.select_by("form", "or")[0]
n2 = r.select_by("form", "exam")[0].children[0] # "the" near the exam
ci = get_deprel_chain(n1, n2)
print(ci.direct) # prints ''
print(ci.reverse) # prints ''
n3 = r.select_by("form", "fail")[0]
ci = get_deprel_chain(n1, n3)
print(ci.direct) # prints ''
print(ci.reverse) # prints 'cc'
ci = get_deprel_chain(n3, n2)
print(ci.direct) # prints 'obj.det'
print(ci.reverse) # prints ''
Constants
udon2.constants module now provides a number of constants for DEPRELs, FEATS and UPOS tags available within the UD framework. This might be useful to checking the annotation consistency or creating any kind of formal language that uses UD concepts (e.g., template and guard languages described in this article).
Each value in every returned list is an instance of udon2.constants.UniversalToken structure that contains two fields: code - the code name used to tag the UD treebanks (e.g., PronType) and name - the actual name of this feature in plain English (e.g., PronType feature has “pronominal type” as name). Below are some examples.
The defined constants are:
udon2.constants.X_UPOS- the instance ofudon2.constants.UniversalTokenfor each UPOS tagX, e.g. ifX=ADV, thenADV_UPOSconstant is defined for itudon2.constants.X_DEPREL- the instance ofudon2.constants.UniversalTokenfor each DEPRELX, e.g. ifX=nsubj, thenNSUBJ_DEPRELconstant is defined for itudon2.constants.X_UFEAT- the instance ofudon2.constants.UniversalTokenfor each universal featureX, e.g. ifX=PronType, thenPRONTYPE_UFEATconstant is defined for itudon2.constants.UPOS_TAGS- the immutable list of all UPOS tags in the UDudon2.constants.DEPRELS- the immutable list of all DEPRELs in the UDudon2.constants.FEATS- the map of all FEATS from theircodes to the lists of possible values
import udon2.constants as uc
print(str(uc.ADV_UPOS)) # prints 'ADV/adverb'
print(str(uc.NSUBJ_DEPREL)) # prints 'nsubj/nominal subject'
print(str(uc.PRONTYPE_UFEAT)) # prints 'PronType/pronominal type'
print([str(x) for x in uc.UPOS_TAGS])
# prints ['ADJ/adjective', 'ADV/adverb', 'ADP/adposition', 'AUX/auxiliary', 'CCONJ/coordinating conjunction', 'DET/determiner', 'INTJ/interjection', 'NOUN/noun', 'NUM/numeral', 'PART/particle', 'PRON/pronoun', 'PROPN/proper noun', 'PUNCT/punctuation', 'SCONJ/subordinating conjunction', 'SYM/symbol', 'VERB/verb', 'X/other']